p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
What is P-Hydroxybenzaldehyde, cas no:123-08-0,a producer telling you the result.
If you need the products .Please send your inquiry to us through e-mail: sales@yuansu-reagent.com
To begin with, let us tell you what is the basic information of P-Hydroxybenzaldehyde ?
Like many stuff, it has many synonyms as follows
First, the chemical is very special, some technical indexes as below
If you need the products .Please send your inquiry to us through e-mail: sales@yuansu-reagent.com
1. Appearance: Colorless crystalline powder with a weak and pleasant aromatic odor.
2. Melting point (º C): 117~119
3. Relative density (g/mL, 130/4 º C): 1.129
5. Relative density (20 ℃, 4 ℃): 1.143117
6. Relative density (25 ℃, 4 ℃): 1.136
7. Refractive index (n130D): 1.5705
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 3980mg/kg; Mouse peritoneal LD50: 500mg/kg
2. Mutability: Human lymphocyte dual chromosome exchange testing system: 1mmol/L
3. Irritating to eyes, respiratory system, and skin.
1. Molar refractive index: 34.88
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 99.5
3. Waiting for Zhang Biarong (90.2K): 367.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 52.0
5. Polarization rate (10-24cm3): 13.83
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: 4
6. Topological molecule polarity surface area 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 93.1
10. Number of isotopic atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Nature and stability
1. Colorless crystalline powder. Easy to sublime in the air. There is a fragrant smell.
2. This product has strong irritant and corrosive properties, with a lethal dose of 3000mg/kg for intraperitoneal injection in guinea pigs and 3000mg/kg in rats
The oral LD50 is 2700mg/kg.
3. Exists in tobacco leaves and smoke.
Second, the Synthetic Route we will recommend is the most important for your reference?
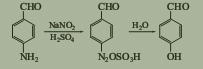
First, synthesis line of P-Hydroxybenzaldehyde CAS NO.123-08-0 as follows
Manufacturing method:
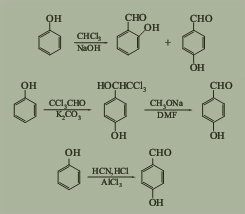
3. The catalytic oxidation method for p-cresol involves the direct oxidation of p-cresol to p-hydroxybenzaldehyde using air or oxygen under the action of a catalyst. In the 1980s, Japan, the United States, Germany, and others conducted in-depth research and reporting on this process route. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, several research and production units in Jiangsu, Shanghai, Dalian and other places in China also conducted research and development on this process and applied it to industrial production. The specific process flow is as follows: add p-cresol, sodium hydroxide, and methanol to a stainless steel pressure vessel, stir until completely dissolved, add cobalt acetate to seal the reaction vessel, raise the temperature to 55 ℃ and start introducing oxygen to maintain the pressure inside the vessel at 1.5 MPa for 8-10 hours. During the reaction process, the oxygen flow rate is strictly controlled, and a coil cooling system is equipped inside the vessel. When the temperature rises during the reaction, cooling water can be passed through the jacket of the vessel. At this time, cooling water begins to flow through the coil, and the total amount of oxygen flow is strictly controlled while maintaining the temperature inside the vessel at around 60 ℃. At the end of the reaction, place the material into the initial distillation kettle, evaporate the solvent methanol for recycling, dissolve it in water, and add hydrochloric acid for salt precipitation. Filter the solid-liquid material using a centrifuge, and place the obtained solid in a vacuum oven to dry at around 60 ℃ for 3-5 hours to obtain p-hydroxybenzaldehyde with a content greater than 98%.
4. Obtain needle crystals from water.
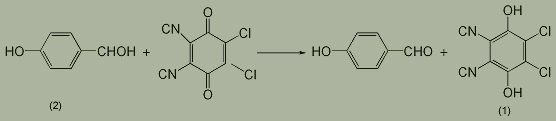
5. Manufacturing method:
Third, what is the usage of P-Hydroxybenzaldehyde CAS NO.123-08-0 ? pleas see below
If you need the products .Please send your inquiry to us through e-mail:sales@yuansu-reagent.com
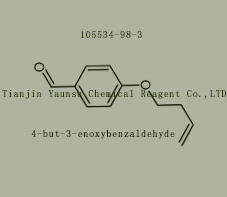
Used for the synthesis of 4-but-3-enoxybenzaldehyde,Cas no. 105534-98-3
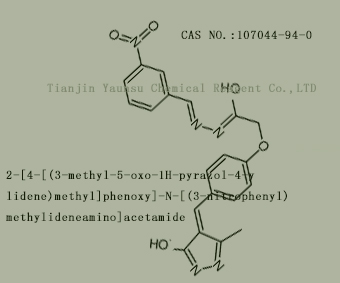
Used for the synthesis of 2-[4-[(Z)-(3-methyl-5-oxo-1H-pyrazol-4-ylidene)methyl]phenoxy]-N-[(3-n
itrophenyl)methylideneamino]acetamide,Cas no. 107044-94-0
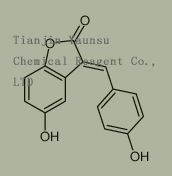
Used for the synthesis of 5-hydroxy-3-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-1-benzofuran-2-one Cas no. 107680-50-2
Besides Safety Information of P-Hydroxybenzaldehyde CAS NO.123-08-0 is also important when handling it
|
Hazard Codes |
Xi |
|
WGK Germany |
3 |
|
H.S.Code: |
2912499000 |
|
TSCA |
Yes |
|
HazardClass |
IRRITANT |
What is the appearance of P-Hydroxybenzaldehyde CAS NO.123-08-0? Please see the picture ofP-Hydroxybenzaldehyde CAS NO.123-08-0, below
If you need the products .Please send your inquiry to us through e-mail: sales@yuansu-reagent.com
Specification ofP-Hydroxybenzaldehyde CAS NO.123-08-0, is below
Apperance: Colorless crystalline powder with a weak and pleasant aromatic odor
Assay: >98.0%(HPLC)
IR identity: conform
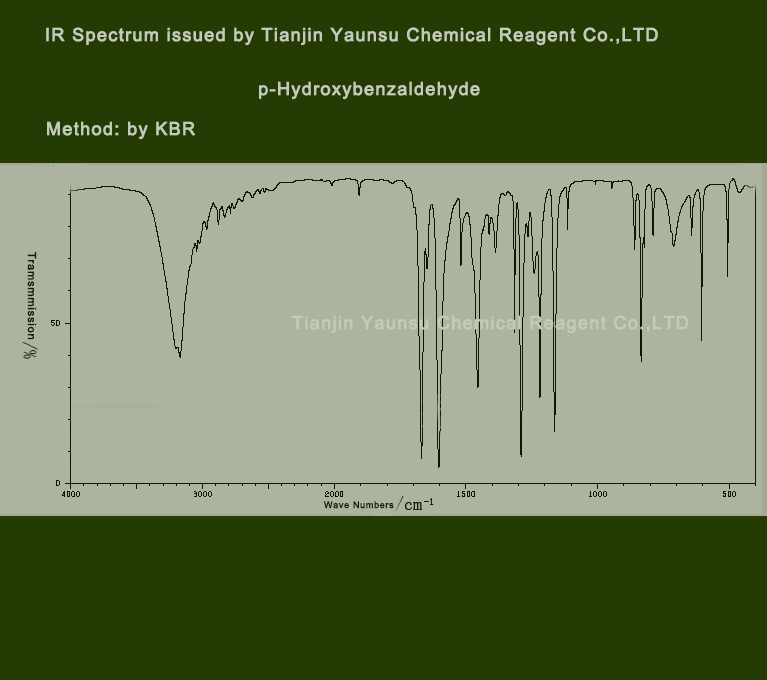
IR Spectrum picture of P-Hydroxybenzaldehyde CAS NO.123-08-0 is as follows,
H-NMR Spectrum picture of P-Hydroxybenzaldehyde CAS NO.123-08-0 is as follows,
Reference of Article cited for your reference below,
(1)
Soil microorganisms: An important determinant of allelopathic activity
Publication Date: 2005
Publication Name: Root Physiology: from Gene to Function
(2)
Potential Role of Dissimilatory Iron Reduction in the Early Evolution of Microbial Respiration
Publication Date: 2004
Publication Name: Origins
(3)
Publication Date: 1972
Publication Name: Epitaxy Data of Inorganic and Organic Crystals